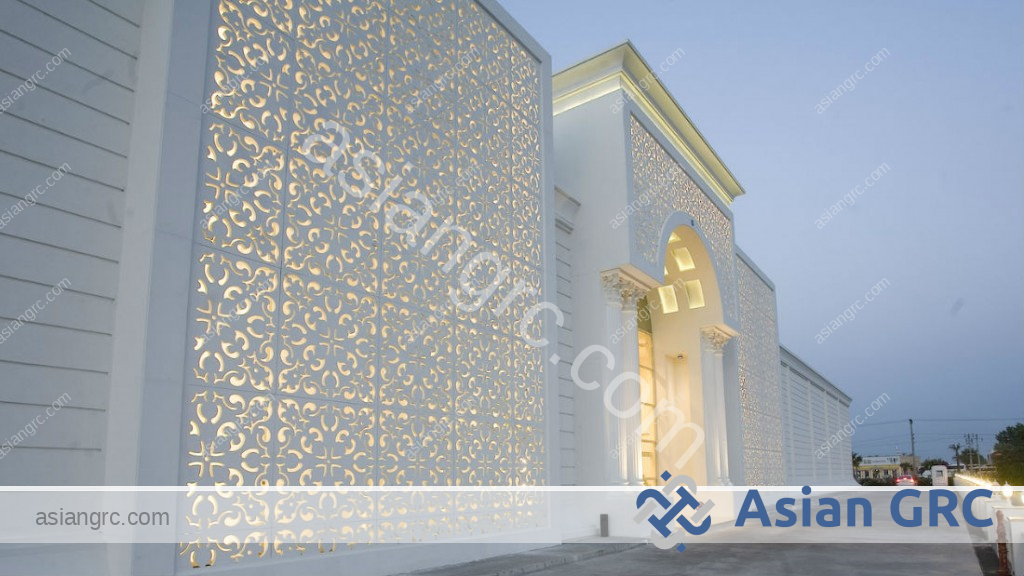
Introduction
In this article, we’ll explore GFRC history, manufacturing process, advantages, applications, Uses and Benefits.
What Does GFRC Stand For?
Glass Fiber Reinforced Concrete. It is a composite material made of cement, fine aggregate, water, and glass fibers.
History of GFRC
The origins may be traced returned to the 1940s when researchers started experimenting with reinforcing concrete with various materials. However, it turned into within the 1970 that Glass Fibre Reinforced Concrete received vast interest inside the production industry.
Key Components of GFRC
Understanding the composition: The primary components include cement, glass fibers, water, and additives. The proportion and quality of these components play a vital role in determining the final properties.
Manufacturing Process of GFRC
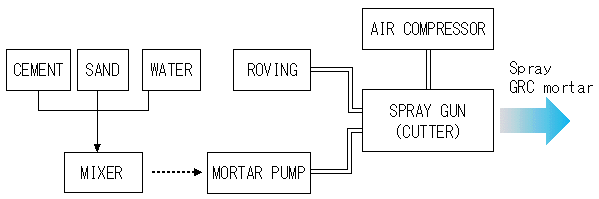
The manufacturing process involves meticulous steps to ensure the proper distribution of glass fibers throughout the concrete matrix.
Advantages of GFRC
Multitude of advantages are exceptional strength, durability, and design flexibility. Architects and designers appreciate the ability it can be molded into intricate shapes, providing endless possibilities for creative expression.
Applications of GFRC
Applications in various fields, ranging from construction to artistic creations. Architectural elements such as facades, cladding, and countertops benefit from the material’s lightweight nature and adaptability.
Comparisons with Traditional Concrete
It offers reduced weight, increased flexibility, and better crack resistance. These factors make it a preferred choice in projects where traditional concrete may fall short.
GFRC in the Modern Architectural Landscape
The integration of GRC jali in modern architecture is exemplified by numerous noteworthy structures. From iconic buildings to public art installations, it has proven its worth in shaping the contemporary aesthetic landscape.
Sustainability Aspects
As sustainability becomes a focal point in construction, it stands out as an environmentally friendly option. The use of glass fibers reduces the need for traditional reinforcement materials, contributing to a more sustainable construction industry.
Future Trends in GFRC Technology
Looking ahead, the future of this technology appears promising. Ongoing research and development focus on enhancing the material’s properties, reducing costs, and expanding its applications.
Tips for Working with GRC
For construction professionals looking to incorporate Glass fiber into their projects, it’s essential to follow best practices. Proper mixing, application techniques, and curing procedures are key factors in achieving optimal results.
GFRC Maintenance
Maintaining its structures is relatively straightforward. Regular cleaning and inspections can help preserve the material’s appearance and structural integrity.
Conclusion
Its unique properties and versatile applications make it a sought-after material for architects, designers, and builders alike. As the industry continues to evolve, GRC is set to play a significant role in shaping the structures of tomorrow.

